38 understanding fat on nutrition labels
Understanding Nutrition Labels: LabelCalc Using Online Nutrition Analysis Software to Create Your Nutrition Label While it is certainly important to understand nutrition labels, it's not worth stressing over every little detail. With FDA-compliant online nutrition analysis software, you really only need to enter your recipe using the software's database and serving size , then the ... Food Labels 101: Understanding the Nutrition Facts Label Nutrition labels can be a great tool for managing a heart healthy diet, which makes it very important that you understand what you're looking at when you read a label. Nutrition labels are based on a daily 2,000 calorie diet. Depending on your age, gender and activity level, you may need to consume more or less than 2,000 calories per day, so ...
Understanding the Nutrition Facts Label - Know Diabetes by Heart Fats Although fat can also contribute to changes in your blood sugar, they have less influence than carbs. However, it is important to reduce amount of saturated and trans fats as a part of a balanced diet. Replacing foods that are high in saturated fat with healthier options can lower blood cholesterol levels and improve lipid profiles. Sodium
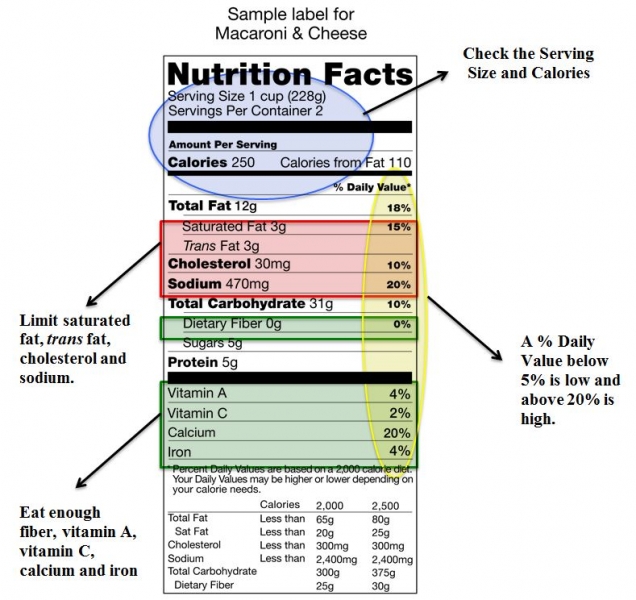
Understanding fat on nutrition labels
Nutrition Education - Action for Healthy Kids Social Awareness: Nutrition education serves as an opportunity to teach children about food and the relation to culture and family heritage. Discussing culinary variances across cultures helps expose children to different foods and traditional practices, increasing their understanding and appreciation for diversity. Food Labels | CDC - Centers for Disease Control and Prevention If you eat the whole thing, you are eating 8 times the amount of calories, carbs, fat, etc., shown on the label. Total Carbohydrate shows you types of carbs in the food, including sugar and fiber. Choose foods with more fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Choose foods with lower calories, saturated fat, sodium, and added sugars. Avoid trans fat. Looking at labels - British Nutrition Foundation The table below shows how high, medium and low levels of fat, saturates, total sugars and salt in foods are classified for front of pack labels (there are different levels for drinks). These levels have been decided by the UK government. The 'per portion' in red is used where portions are 250g or more. What are reference intakes?
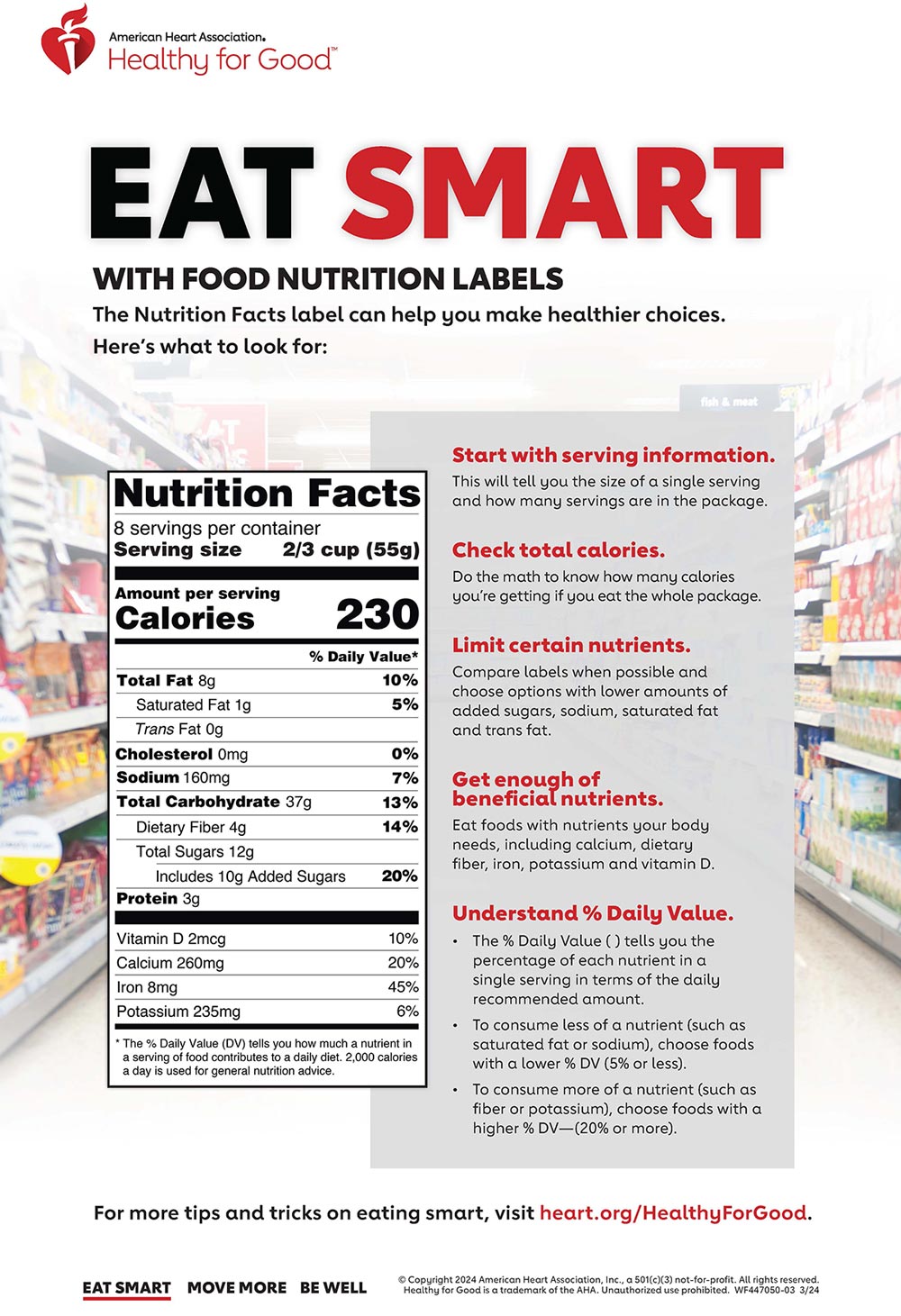
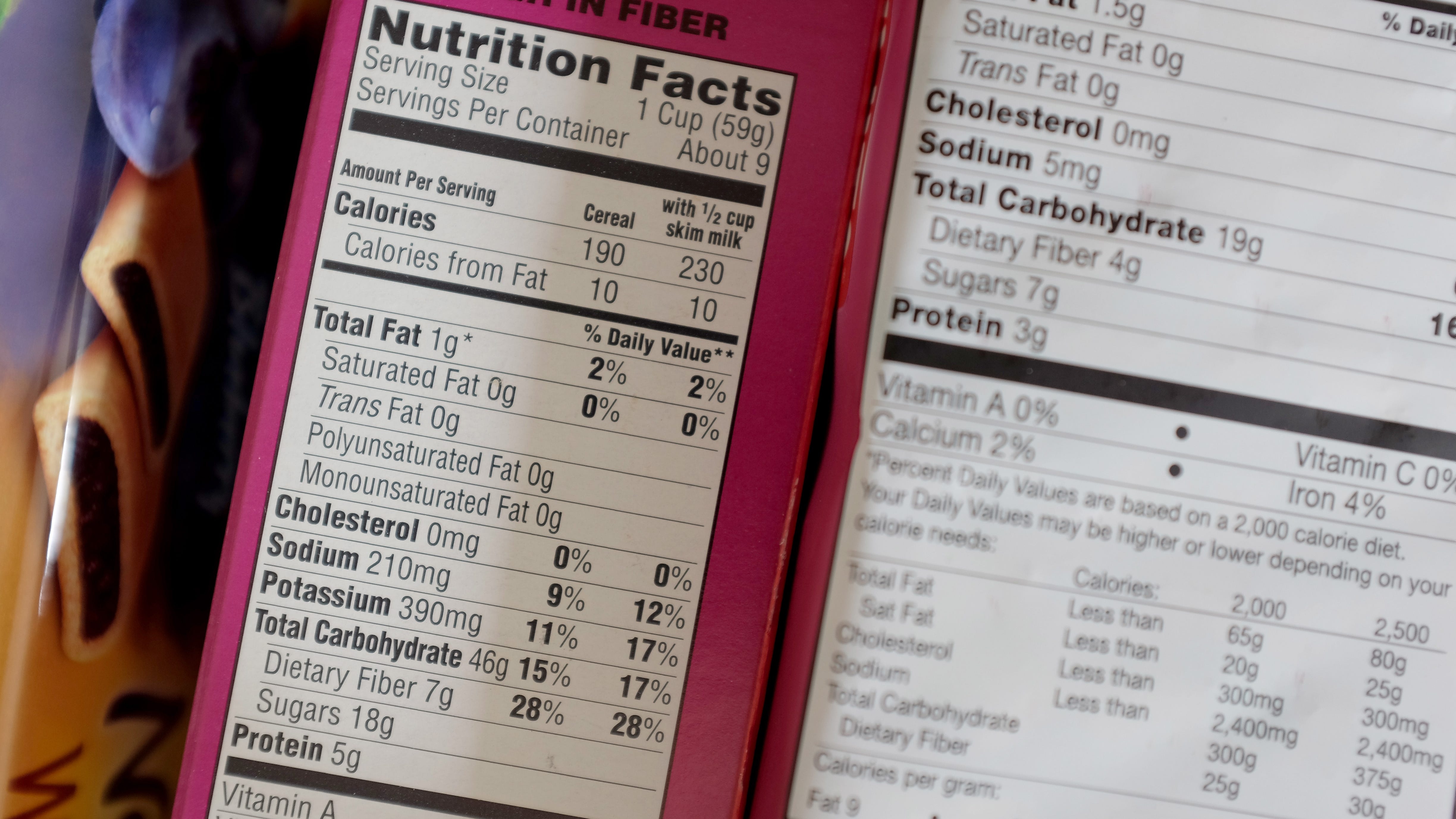
Understanding fat on nutrition labels. Understanding Food Nutrition Labels | Sanford Fit Nutritional Information When looking at fat, carbohydrates, sodium, added sugar, and vitamins, the percent Daily Value (%DV) is a good guide. The percent Daily Value (%DV) will show how much of a nutrient is in a serving of food and contributes to a total daily diet. A general guide: 5% DV or less of a nutrient per serving is considered low. Interpreting Total Fat and Types of Fat on Food Labels - Nina Cherie ... Now, at the end of the day, since all high-fat foods tend to drive up calorie counts, it's typically recommended that you limit your intake of total fat to 25-35% of your daily calories. Of this amount, saturated fats and trans fats should comprise less than 7-10% and no more than 1%, respectively. Understanding Food Nutrition Labels | Go Red for Women 5 - Understand % Daily Value. The % Daily Value (DV) tells you the percentage of each nutrient in a single serving, in terms of the daily recommended amount. If you want to consume less of a nutrient (such as saturated fat or sodium), choose foods with a lower % DV (5 percent or less). If you want to consume more of a nutrient (such as fiber ... Understanding Food Nutrition Labels | EmPOWERED To Serve When the Nutrition Facts label says a food contains "0 g" of trans fat, but includes "partially hydrogenated oil" in the ingredient list, it means the food contains some trans fat, but less than 0.5 grams per serving. So, if you eat more than one serving, you could end up eating too much trans fat.
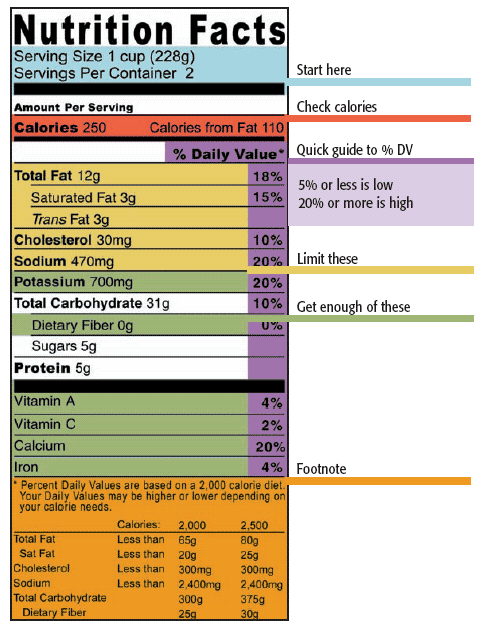
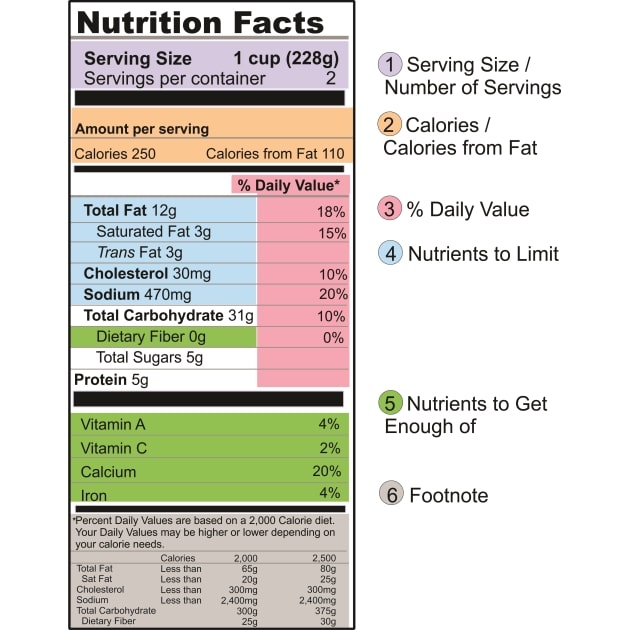
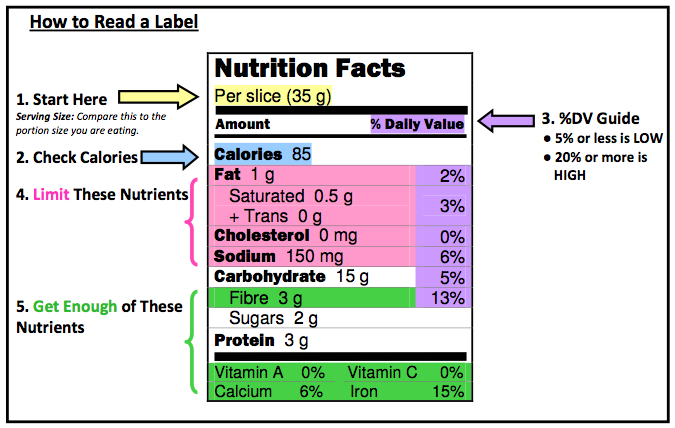
Reading and understanding nutrition labels - Prospect Medical DVs are based on a 2,000-calorie diet for healthy adults. A rule of thumb is that any 5% DV or less is low, and 20% or more is high. Know your fats. Look for foods low in saturated and trans fats, and cholesterol, to help reduce the risk of heart disease. Trans fat is considered by many doctors to be the worst type of fat you can eat. Understanding Nutritional Labels | Beaumont | Beaumont Health Here are the parts of most food labels: Calories (total calories and calories from fat) - This part of the label tells you how many calories each serving has and how many of those calories come from fat. Total Fat - Total fat is the number of fat grams per serving. There are different types of fat. Some are good for you and some aren't. Understanding Ingredients on Food Labels | American Heart ... Mar 06, 2017 · Understanding Ingredients on Food Labels Food labels are an important source of information about calories and the nutritional value of the foods you eat, a crucial tool in building a heart-healthy diet. Understanding Food Nutrition Labels | American Heart Association When the Nutrition Facts label says a food contains "0 g" of trans fat, but includes "partially hydrogenated oil" in the ingredient list, it means the food contains some trans fat, but less than 0.5 grams per serving. So, if you eat more than one serving, you could end up eating too much trans fat.
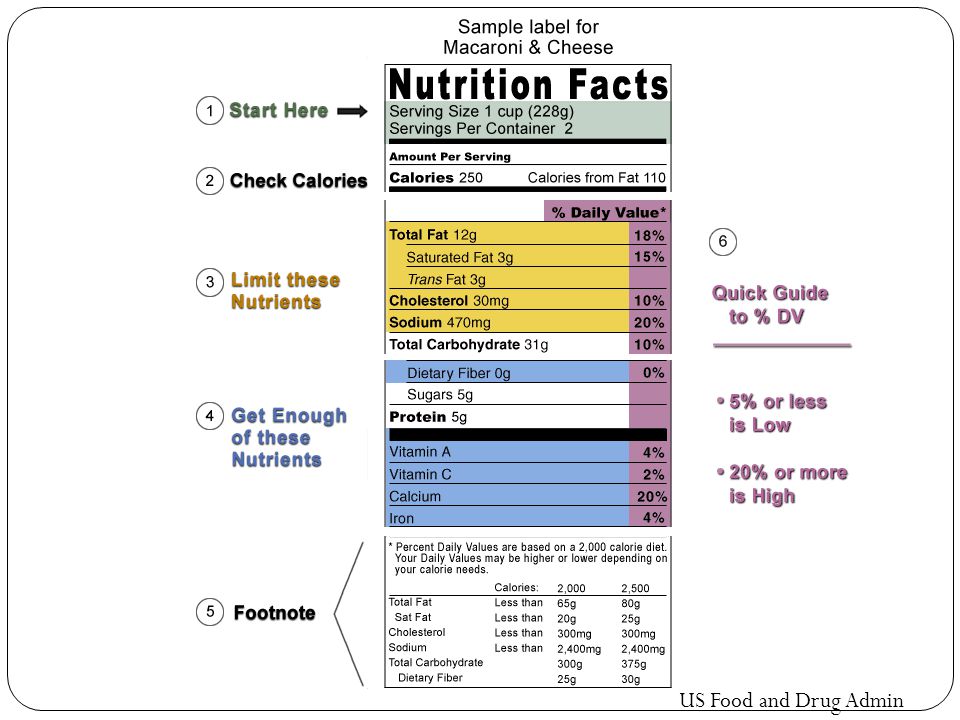
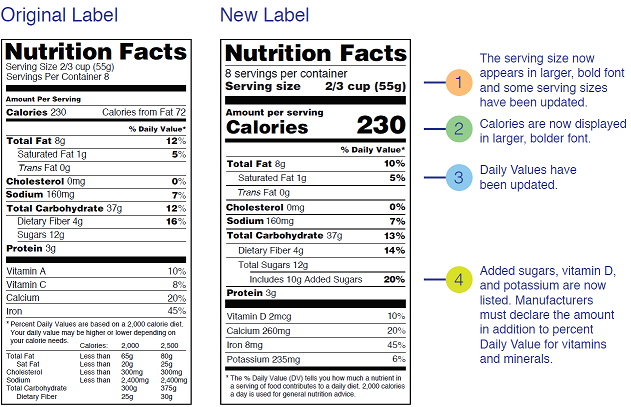
Food labels - NHS These labels provide information on the number of grams of fat, saturated fat, sugars and salt, and the amount of energy (in kJ and kcal) in a serving or portion of the food. But be aware that the manufacturer's idea of a portion may be different from yours. Some front-of-pack nutrition labels also provide information about reference intakes. Learn How the Nutrition Facts Label Can Help You Improve Your Health Calories & Fat Larger, darker letters make calories the easiest item to see. When it comes to health outcomes, the type of fat you eat matters more than the overall amount of fat. For this reason, the label shows percentages of calories from unhealthy saturated and trans fats rather than the percentage of calories from all fat. Added Sugars The Basics of the Nutrition Facts Label Step 4: Check Out the Nutrition Terms. Low calorie: 40 calories or less per serving. Low cholesterol: 20 milligrams or less and 2 grams or less of saturated fat per serving. Reduced: At least 25% less of the specified nutrient or calories than the usual product. Good source of: Provides at least 10 to 19% of the Daily Value of a particular ... Get the Facts! Steps to Reading and Understanding Nutrition Facts Labels Steps to Reading and Understanding Nutrition Facts Labels (FN1404, Reviewed Feb. 2022) File. Publication File: FN1404. ... Eating too much saturated fat and/or trans fat, for example, may increase your risk of heart disease. Carbohydrates. Check the amounts of dietary fiber, vitamin D, calcium, iron and potassium.
How to Read the Nutrition Facts Label on Packaged Foods - WebMD Sodium. Many people get far too much salt, or sodium. Most of it is in packaged foods and restaurant items. Limit salt to 2,300 milligrams (about 1 teaspoon) daily. If you have high blood pressure ...
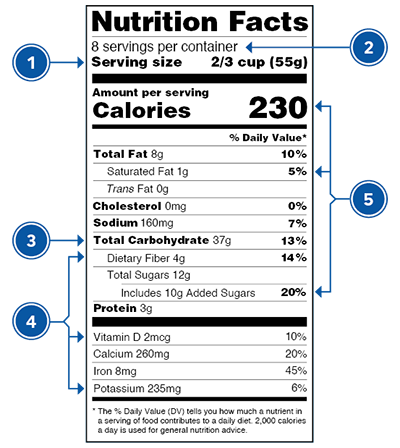
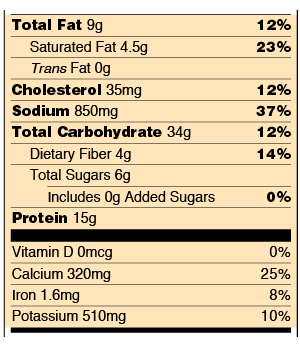
How to Understand and Use the Nutrition Facts Label | FDA Nutrients to get less of: Saturated Fat, Sodium, and Added Sugars. Saturated fat, sodium, and added sugars are nutrients listed on the label that may be associated with adverse health effects - and...
Reading Food Labels | ADA - American Diabetes Association The Nutrition Facts labels on foods are really the key to making the best choices. We'll cover the basics so that these labels make shopping easier for you. You've heard it all. From carb-free to low-carb, to whole and empty carbs, it's hard to know what it all means. Blood sugar highs and lows aren't always easy to understand.
Understanding Nutrition Fact Labels | Penn Highlands Healthcare Understanding Nutrition Fact Labels. One of the best ways to take greater control of your health is by better understanding what you eat and drink in a day. Fortunately, the Nutrition Fact labels on nearly everything we buy gives us this exact information. ... Too much saturated fat and sodium are associated with an increased risk for ...
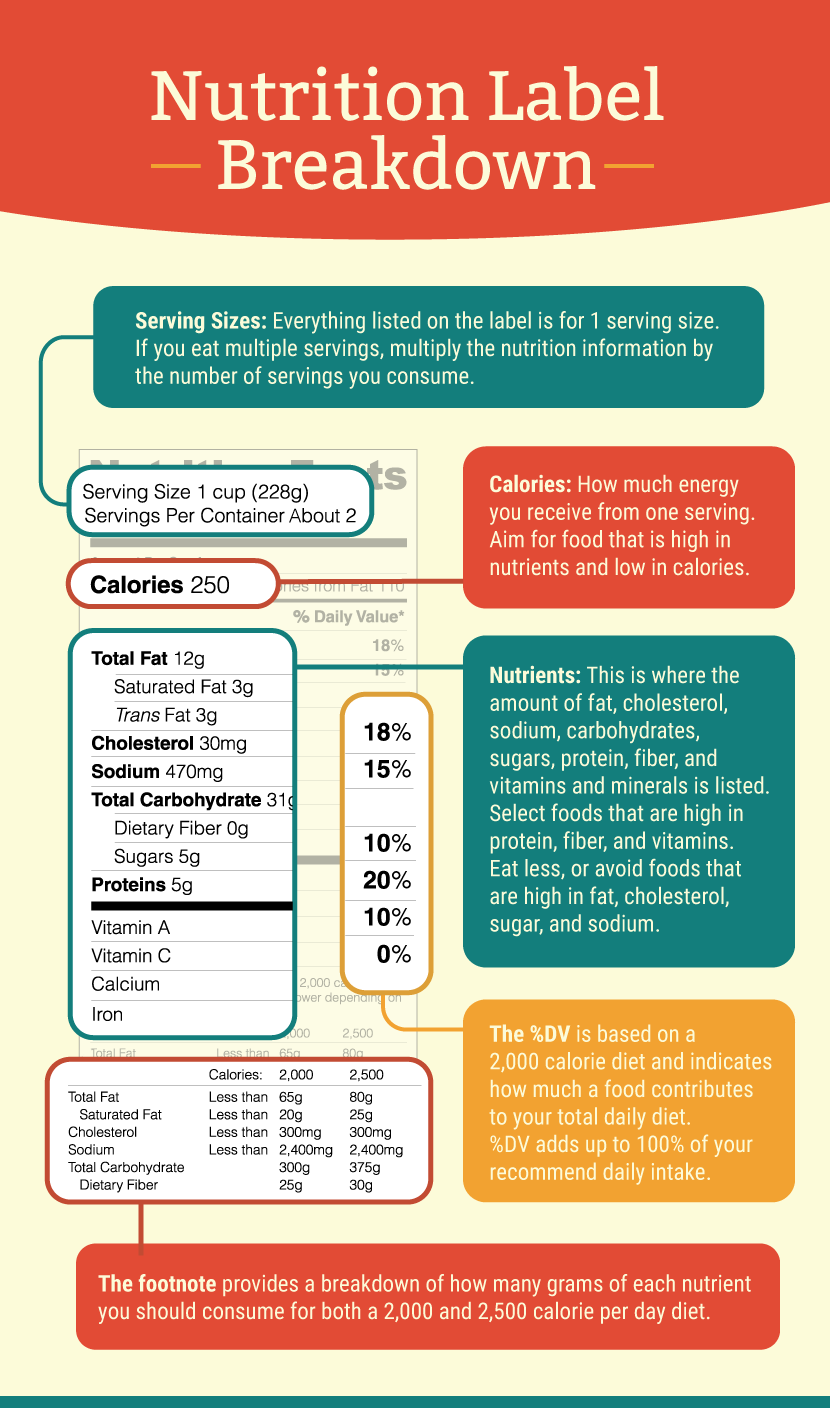
Food Labels: Fat & Cholesterol | Home & Garden Information Center The Nutrition Facts label shows you how much fat is in a product, even if the fat is hidden as an ingredient. The serving size and the nutrients listed on this label are consistent, which makes it easy to compare similar products without any calculations. % Daily Values (% DVs) are listed in a column on the "Nutrition Facts" label.
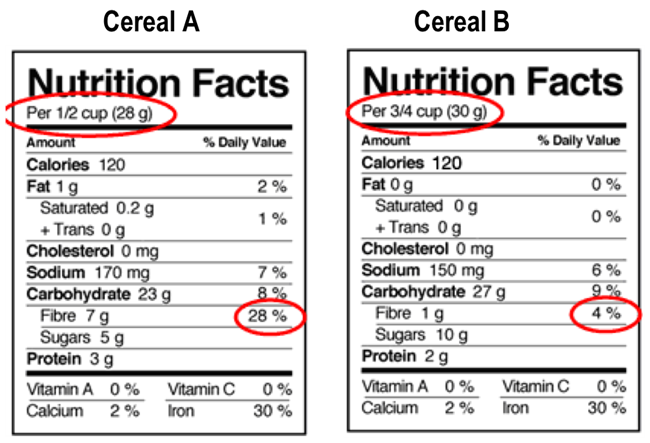
Nutrition label | Tufts Medical Center If the label serving size is 1 cup, and you eat 2 cups, you are getting twice the nutrients listed on the label. Limit Saturated Fat, Trans Fat, Sodium & Added Sugars. Limit saturated fats to <10% of total calories daily. Choose products with monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats, as these are heart healthy.
Food label: ingredient list - Canada.ca Understanding food labels. Nutrition facts tables; Serving size; Food label: ingredient list; Nutrition claims; Nutrient content claims: what they mean; Percent daily value; About food labels; Calories; Health claims: what they mean; Understanding food labels - Interactive tools; Nutrition Labelling Online Course
How to understand food nutrition labels | by Alpha Medical Team | Alpha ... The FDA recommends limiting saturated fat, sodium, and added sugars. On the other hand, it's good to get foods that are high in fiber, vitamin D, calcium, iron, and potassium, as these are some...
Fat Content on Food Labels - Reading Between the Lines The Mayo Foundation continued, "Still, you may be able to tell if a product contains trans fat, even if it's not directly listed on the food label. Look for the words ' hydrogenated ' or 'partially hydrogenated' in the list of ingredients. These terms indicate that the product contains trans fat.
20 Tips for Understanding Nutrition Labels | Eat This Not That Macronutrients include fat, carbs (which also breaks down into fiber and sugar), and protein. If anything stands out to you—like the product having 17 grams of fat or 25 grams of sugar—use those numbers to help you skim the ingredient list. For example, a cereal that has 6 grams of fat in it is odd.
Understanding Food Labels | The Nutrition Source | Harvard T ... Chile implemented the Law of Food Labeling and Advertising in 2016, comprised of mandatory front-of-package (FOP) warning labels, restrictions on child-directed marketing, and the banning of sales in schools of all foods and beverages containing added sugars, sodium, or saturated fats that exceeded set nutrient or calorie thresholds. [1]
How to understand food labels | Eat For Health The Nutrition Information Panel on a food label offers the simplest and easiest way to choose foods with less saturated fat, salt (sodium), added sugars and kilojoules, and more fibre. It can also be used to decide how large one serve of a food group choice or discretionary food would be and whether it's worth the kilojoules.
Nutrition Facts Label: Understanding the Label | Extension | University ... Calories refers to the total number of calories, or "energy," supplied from all sources (fat, carbohydrate, protein, and alcohol) in one serving of the food. As a general guide: 100 calories per serving of an individual food is considered a moderate amount, and 400 calories or more per serving of an individual food is considered high in calories.
Looking at labels - British Nutrition Foundation The table below shows how high, medium and low levels of fat, saturates, total sugars and salt in foods are classified for front of pack labels (there are different levels for drinks). These levels have been decided by the UK government. The 'per portion' in red is used where portions are 250g or more. What are reference intakes?
Food Labels | CDC - Centers for Disease Control and Prevention If you eat the whole thing, you are eating 8 times the amount of calories, carbs, fat, etc., shown on the label. Total Carbohydrate shows you types of carbs in the food, including sugar and fiber. Choose foods with more fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Choose foods with lower calories, saturated fat, sodium, and added sugars. Avoid trans fat.
Nutrition Education - Action for Healthy Kids Social Awareness: Nutrition education serves as an opportunity to teach children about food and the relation to culture and family heritage. Discussing culinary variances across cultures helps expose children to different foods and traditional practices, increasing their understanding and appreciation for diversity.









/Untitled-design-1--5755c3703df78c9b46903dab.jpg)











Post a Comment for "38 understanding fat on nutrition labels"